30-second summary:
There have been three core updates in 2021, released in June, July, and November, while another was rumored but unconfirmed in OctoberFeatured snippets that fell under the YMYL algorithm were unexpectedly removed in February, then restored in MarchProduct reviews came under the microscope in April, with marketing and sales-centric language penalized in favor of expertise on review-centric websitesMultiple spam updates unfolded throughout the year, though these updates should not impact any website that follows Google’s guidelines
Successful SEO strategy is akin to dancing the tango with Google updates. Unfortunately for copywriters, the Big G can be an unpredictable partner at times. In addition to daily algorithm tweaks that go unnoticed, we all brace ourselves for core updates that have a sizeable impact on page ranking and performance. Throughout 2021, Google has confirmed a handful of updates.
Further updates have also been speculated by experienced web-based professionals, reporting these to aid others in remaining on the right side of an adjustment. Throughout this guide, we’ll discuss the updates rolled out by Google in 2021 to date.
Complete list of 2021 Google updates
As promised, let’s review all the algorithm updates issued by Google during 2021, major and minor alike. Some of these are official, confirmed by Alphabet themselves. The core updates are an obvious example of this. Others were noticed by webmasters of influential brands and discussed online. These unconfirmed updates are marked in red below.
1. Passage indexing (February)
The passage indexing update, announced in October 2020, is probably better described as passage ranking. The purpose behind the update is simple and noble. It will pick out one particular sentence or paragraph from a long-form article, aiding a niche web query and avoiding irrelevance.
Essentially, this update seeks out keywords and terminology in an entire article rather than focusing primarily on titles and subheadings. At the time of writing, Google projects that this will impact around 7 percent of search queries. At this point, the passage indexing update also only applies to copy written in US English, though this will eventually become global and translingual policy.
Now, you may be wondering how this differs from a featured snippet. The short answer is that a snippet is chosen based on the whole web page, seeking relevance to the subject at hand in all aspects of the query. The passage indexing update can pick up on a small element of a broader discussion that would otherwise be banished to the mid-page and beyond. Speaking of featured snippets, however…
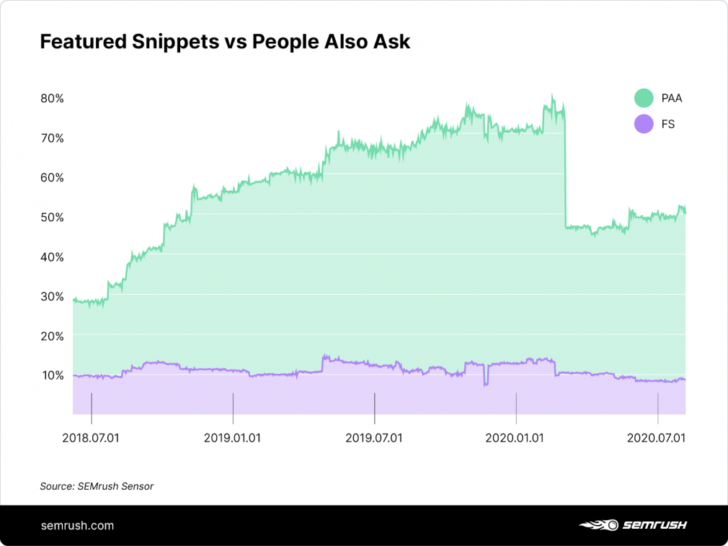
2. Featured snippet drop/featured snippet recovery (February and March)
In mid-February, MozCast noticed that featured snippets vanished from countless SERPs on Google. This involved a decline of some 40 percent, the largest in over six years. Snippets that revolved around medical or financial advice were particularly impacted. Some of the keywords and terms that experienced this plummet included:
AcneAutismDiabetesFibromyalgiaInvestmentIRALupusMutual fundsPensionRisk management
As you’ll see, the YMYL broad algorithm appeared to be a particular bone of contention. We’ll never know for sure, as this update – if indeed there was an update – has never been confirmed or denied by Google. What’s more, around a month later, these snippets returned as though they had never been away.
Without any explanation behind the mystery, it’s impossible to offer advice to webmasters on how to avoid a future unwarned absence of featured snippets. The fact that YMYL was hit so hard suggests that it was a deliberate action, though. Whenever working within this niche, proceed with caution – especially if relying on SERPs for ecommerce opportunities.
3. Product review update (April)
April’s product review update was also critical to ecommerce sites and those that collate product insights. Google is adamant that this has not been a core update. However, the approach that content marketers must now take mirrors the core updates that arose later in the year.
Following the review update, it’s more important than ever that product reviews remain strictly factual. That means discussing a product’s qualities (or lack thereof) without clear and obvious attempts to push for a sale from an affiliate. Sites that used their copy to talk up the qualities of a product using popular keywords and directing consumers toward Amazon were typically penalized.
Thin copy, as always, captured Google’s attention too, and not in a positive manner. Meaningless, fluffy words designed to pad out a page, along with repetition, will see a page slide down the rankings. A product review site that hopes to remain in good stead with Google must remember the fundamental rules of E-A-T. You can still attempt to make a sale, but not at the expense of demonstrating expertise, authority, and trustworthiness.
4. Multitask Unified Model aka MUM (June)
June was a busy month for Google, starting with the Multitask Unified Model update, better known as MUM. This update could be considered a logical extension of the previously discussed passage indexing update. MUM also used AI to improve the search experience for users, replacing BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers).
It’s claimed that MUM is at least 1,000 times more powerful than its predecessor. In addition to providing greater, much more insightful data for users, MUM works to eradicate language barriers, including misspellings, leaning upon nuance to meet the expectations of a search.
Perhaps more importantly, MUM means that irrelevant content, picked up through a questionable use of keywords to game the SEO system, will soon disappear from the top of the page in favor of more appropriate content. The core update that came later in the month garnered most of the headlines, but don’t sleep on the impact of MUM.
5. Spam updates (June)
Next in June came a spam update, which took place over two weeks. In theory, this update should not have impacted any website operating under white hat SEO rules. It was designed purely to keep content relevant and appropriate, battling against sinister tactics.
As always, though, there was room for error with this update. It’s always advisable to keep on top of the latest webmaster guidelines laid out by Google. This way, a site is considerably less likely to fall foul to a misunderstanding and accusations of black hat traffic-hoarding.
Updates to Google’s Predator algorithm could also be considered a crucial part of this update. Google has been taking lengths to protect people from harassment online, and a big part of this is downgrading sites that seemingly exist purely to denigrate a reputation.
6. Page experience update (June)
Page experience update sounds like a grand event, comparable even to a core update. In reality, this was a pretty low-key affair. It was also a slow procession, kicking off in June and rumbling on until August. All the same, there will be a degree of ebb and flow as a result. Discuss the update with your UX designer and ensure it remains at the forefront of your thinking.
One of the biggest takeaways from this update is that AMP is no longer essential to rank as a top new story. That could make a sizeable difference to any reporting site. The usual caveats still apply, though – sticking to the established policies of Google News is non-negotiable. Although AMP is no longer critical, ensure your news articles remain mobile-friendly, hosted on a fast and secure server, and unfold devoid of interruptions such as intrusive advertising.
7. Core update (June and July)
Here’s the big kahuna that has every web admin across the globe on tenterhooks – Google’s major summer core update. In 2021, Google announced two updates over June and July, both of which would be connected.
As always, there were winners and losers from this update. In a recurring theme, YMYL sites appeared to lose a great deal of traffic throughout the update – especially in June, when the changes were most volatile. Thin content in any niche also seemed to be a particular focus of this update, with such sites pruned cautiously.
However, some sites that were previously heavily penalized may have experienced a little bounce back. It has been claimed that the biggest priorities of the June and July updates, other than thin copy, have been domain age and the use of backlinks.
Review the traffic of any old sites that you wrote off after the game-changing updates of 2019. These sites may have experienced a revival in page ranking and could be worth reinvestment. Just be mindful that Google may consider this an oversight and reverse the decision at any moment.
8. Link spam update (July)
Another spam-detecting algorithm rolled out in July, this time focusing on backlinks. What’s interesting here is that Google referred to this update as ‘nullifying’ spam links, not penalizing them.
Essentially, Google will just stop counting inappropriate links toward a page ranking and quality score. Naturally, though, it would feel like a punishment if a site relied upon these links previously – this is an important Google update for link-building professionals to pay attention to.
Keep an eye on the links on your site if you have seen a drop in traffic, ensuring that they meet Google’s link scheme standards. It could be all too easy to fall foul to this update based on outdated copy that has not been updated in some time and now links to an altered and irrelevant online location.
9. Page title rewrites (August)
Here’s an interesting update from August. Google started to adjust carefully selected page titles, leading to different ‘headlines’ in search results. This may have SEO consultants across the world wailing and gnashing their teeth, seeing meticulously curated messaging adjusted according to Google’s whims.
Rest assured, the page titles are not undertaking complete rewrites. We are talking about adjustments, not wholesale changes, to title tags. All the same, it could be enough to leave a webmaster frustrated with the outcome. Nobody wants to be accused of click-baiting, especially when the news industry has a questionable reputation with a cynical population segment.
There is little anybody can do to prevent this. To retain some measure of control, though, keep your H1 headings short and readable, and be mindful of your H2 headings. These may be used, in part or whole, to adjust the title of a search result.
10. Speculated core update (October)
We previously discussed how, back in February, MozCast acknowledged some strange patterns pertaining to featured snippets that Google never acknowledged. Something similar unfolded in October when various significant webmasters noted sizeable changes in traffic and performance. This led to claims that Google had engaged in another core update.
Much like February, these changes remain unconfirmed. However, as we’ll discuss in a moment, there was a reasonably seismic core update in November. Given that the previous update unfolded over two months, it is not beyond the realms of possibility that Google adopted the same practice this time around.
11. Spam update (November)
Another spam update occurred in November 2021, once again targeting infractions that break Google’s general content guidelines. A website that does not contravene basic regulations or cut SEO corners should remain unaffected. Do keep an eye on your traffic and performance, though. If you notice any fluctuations, it could be time for a refresh of your content.
12. Confirmed core update (November)
Finally, we had another core algorithm update in November. At the time of writing, this was still a very recent development. As a result, the impact of the update will become more apparent over time. Some early responses and acknowledgments have been noted, though.
The most significant adjustment appears to be mobile searches, which were declared 23 percent more volatile than the previous update. Again, much like earlier in the year, featured snippets and ‘quick answers’ in the YMYL niche seem the most heavily impacted. Health and real estate, in particular, have seen a big change in performance.
Now, it’s worth noting here that Google felt compelled to address the timing of this update. Danny Sullivan took to Twitter and accepted that an update just before Black Friday and the Christmas shopping season is not ideal for ecommerce sites – especially those that already adjusted their copy based on previous updates.
Source: Twitter
It will be interesting to see if this will change how Google approaches algorithm updates in 2022 and beyond.
This concludes our trip through the Google algorithm updates of 2021. Just remember, more tweaks and changes are made each day. Most of these adjustments have little to no impact on the performance of your website. If you have spotted a change in fortunes, though, review when this occurred. You may find the answer lies above.
Joe Dawson is Director of strategic growth agency Creative.onl, based in the UK. He can be found on Twitter @jdwn
Subscribe to the Search Engine Watch newsletter for insights on SEO, the search landscape, search marketing, digital marketing, leadership, podcasts, and more.
Join the conversation with us on LinkedIn and Twitter.
The post 2021 Google updates round up: everything businesses need to win at search appeared first on Search Engine Watch.
Did you miss our previous article…
https://www.61seoservices.com/?p=315